
May 09, 2023
how does qr code work
During my research, I visited several sources, including Investopedia, SproutQR, Scanova, The Conversation, and QRCode.com, as well as a relevant Reddit discussion. There was a general consensus on how QR codes work, their differences from barcodes, and their applications. Given the consistency across these sources, I am confident in the information obtained.
Words
503
Time
5m 43s
Contributors
13
Words read
9.5k
Have an opinion? Send us proposed edits/additions and we may incorporate them into this article with credit.
QR Codes and How They Work
Differences between QR Codes and Barcodes
Types of QR Codes
Applications of QR Codes
Avoiding Duplication in QR Codes
Jump to top
Research
 "https://scanova.io/blog/how-qr-codes-work/"
"https://scanova.io/blog/how-qr-codes-work/"
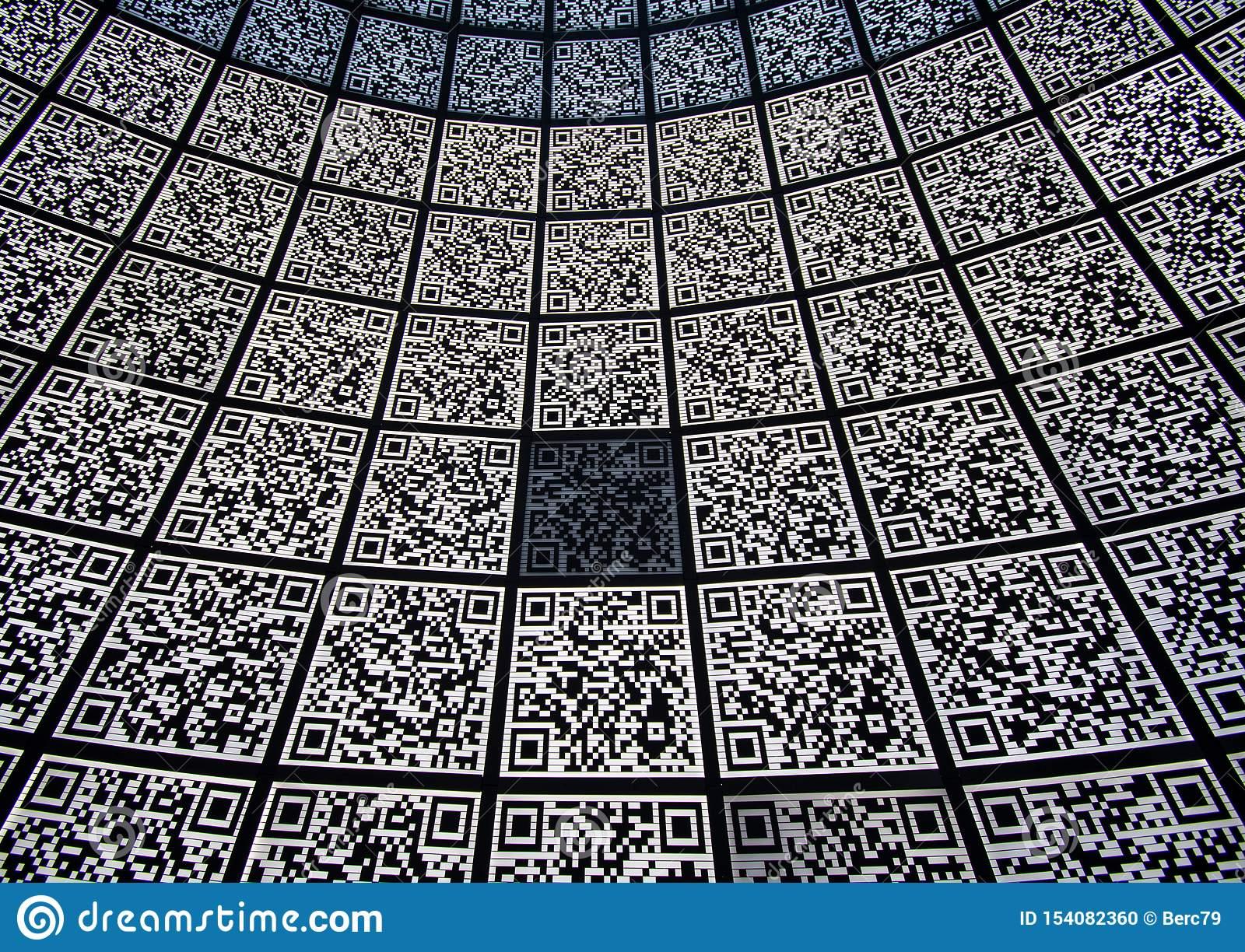
- QR codes are two-dimensional barcodes that were invented by a subsidiary of Toyota called Denso Wave in 1994.
- QR codes work by encoding data in a way that can be easily read by a scanner or a mobile device, which is essentially a language that is not readable by humans.
- QR codes are made up of data modules, which are black-and-white blocks that store data and make up the rows and columns of the QR code. Modules can store data in four different modes: numeric, alphanumeric, binary, and Kanji. The version number of the QR code determines the number of rows and columns of modules, which ranges between 1 and 40, and determines the storage capacity of the QR code.
- The size of the module is determined by the timing pattern, which creates alternating black-and-white modules that help the scanning software understand the width of a single module.
- Finder patterns take up three corners of the QR code and help scanners recognize the QR code accurately and allow them to read the QR code at high speed. Separators help the scanner distinguish between the finder patterns and the actual data. Alignment markers are smaller than position markers and help the scanner determine the orientation of the QR code.
- QR codes must have a quiet zone, which is basically white space around its boundary, and is equal to 4 modules thick. The quiet zone helps the scanner locate the finder patterns.
- Error correction allows the data to remain scannable even if the QR code is somewhat damaged, scratched, or worn out, up to 30%. There are four possible levels of error correction: L–7%, M–15%, Q–25%, and H–30%. Adding error correction increases the number of modules (data blocks) in a QR code.
- Mask patterns make QR codes more readable for scanners, and there are eight possible mask pattern possibilities. Data masking is a way to choose the best possible arrangement of modules that makes it easy for a scanner to decode the QR code. The preferred mask pattern is chosen by calculating a penalty score for each resulting QR code.
- QR codes have a storage capacity of up to 7089 digits or 4296 characters, including special characters. QR code’s scannability largely depends on its elements’ color and the background’s color. It is mandatory to ensure sufficient contrast between the two to ensure proper scanning.
- Scanning a QR code is done by opening a smartphone camera or a third-party QR code scanning app, holding the camera in front of the QR code, and receiving a
 "https://www.investopedia.com/terms/q/quick-response-qr-code.asp"
"https://www.investopedia.com/terms/q/quick-response-qr-code.asp"
- A QR code is a type of barcode that can be read easily by a digital device and stores information as a series of pixels in a square-shaped grid.
- QR codes are frequently used to track information about products in a supply chain and often used in marketing and advertising campaigns. They are considered an advancement from older uni-dimensional barcodes and were approved as an international standard in 2000 by the ISO.
- QR codes were invented by Denso Wave, a subsidiary of Toyota in the 1990s, as a way to track automobiles throughout the manufacturing process.
- One advantage of QR codes over barcodes is that QR codes can be digitally scanned by devices such as mobile phones, while barcodes require a beam of light to bounce off of the parallel lines.
- QR codes can store more information than traditional barcodes and primarily handle four modes of data: alphanumeric, numeric, binary, and Kanji.
- There are a number of QR code types that may be used for different items, including Micro QR Code, Model 1 QR Codes, Model 2 QR Codes, IQR Code, SQRC, and Frame QR.
- Micro QR Code is a smaller version of a traditional QR code used when space is limited. It can encode up to 21 alphanumeric characters.
- Model 1 QR Codes are the prototype of Model 2 and Micro QR. Its maximum data capacity is 468 bytes, which can encode up to 707 alphanumeric characters.
- Model 2 QR Codes contain greater data density than Model 1 and have an alignment pattern for better position adjustment. Its version 40 is capable of storing up to 4,296 alphanumeric characters.
- IQR Code can be created in square or rectangle forms in cases where space or shape is an issue. It can be in any one of 61 formats.
- SQRC features a restricted reading function to contain private information.
- Frame QR is a customizable frame that can contain larger data in formats such as graphics, illustrations, or photos.
- QR codes have not been as popular with consumers as expected and are mostly associated with advertisers and marketing campaigns.
- QR codes are increasingly used to facilitate digital payments and in cryptocurrency systems such as displaying one’s Bitcoin address.
- QR codes are also used to transmit web addresses to mobile phones and have become more widespread in advertising, especially in China and other parts of Asia.
- Several websites provide QR code generators that allow users to create their own QR codes for various purposes.
 "https://www.sproutqr.com/blog/qr-code-uses"
"https://www.sproutqr.com/blog/qr-code-uses"
- QR codes can contain a variety of information, from simple text to complicated interactive experiences such as PDFs, image files, banking information, and authentication/authorization data.
- QR codes are more efficient than barcodes as they hold much more data and can access it faster.
- The agility and portability of QR codes mean they can be displayed almost anywhere, including product packaging, advertisements, websites, and storefronts.
- QR codes on touchless menus and touchless ordering in restaurants provide a hygienic and contactless solution to avoid paper menus, and they save on paper and printing costs. They are quickly becoming a common piece of restaurant technology.
- Touchless payments using a QR code can be integrated into the restaurant experience alongside digital menus and touchless ordering solutions, resulting in an entirely contactless commercial experience.
- Taking attendance using QR codes records information associated with each scan, including the device, classroom number, and date. Attendees can input their names when prompted, and all information exports to a spreadsheet.
- QR codes can be used for checking in and making reservations, and patients can be identified using unique QR codes assigned to them.
- In healthcare, QR codes provide information on drug safety, side effects, and usage, as well as medical equipment information.
- QR codes are used in libraries to provide library information and research assistance suggestions, and in some cases, provide a QR-based mobile library service.
- QR codes can contain basic operational or contact information such as hours of operation, rules and procedures for campsites, hotels, or tours, exhibit schedules for museums, or holidays closed for banks.
- QR codes can be used for customer feedback surveys, providing a digital distribution method and potential for a great response.
 "https://www.sproutqr.com/blog/how-do-qr-codes-work"
"https://www.sproutqr.com/blog/how-do-qr-codes-work"
- A QR code is a type of barcode that can be scanned to access information encoded in it.
- QR codes are different from standard barcodes in that information is encoded in the arrangement of squares in QR codes as opposed to the width of and distance between vertical lines in standard barcodes.
- QR codes can hold more data than standard barcodes.
- Data can be encoded in QR codes using numeric and alphanumeric characters, bytes, and kanji.
- QR codes can be scanned by virtually all smartphones, making them easily accessible.
- A QR code is essentially a scannable barcode that is encoded with data.
- The data contained in a QR code can be converted into a unique two-dimensional arrangement of squares, allowing it to be scanned by an optical scanner and translated back to its original form.
- The characters in a QR code are encoded into squares called data modules. These data modules make up the majority of a QR code.
- There are three position markers on every QR code that allow scanners and cameras to accurately locate the data modules and scanning direction.
- The blank area on all sides of the data module matrix is called the quiet zone, and it allows scanners and readers to optically identify where the QR code begins and ends.
- The size of a QR code corresponds to its version. The smallest QR code is version 1, which is 21 rows by 21 columns. The largest possible QR code is version 40, which is 177x177.
- QR codes can store up to 7,089 numeric characters or 2,953 alphanumeric characters, bytes, and kanji.
- There is a dynamic version of QR codes in which the encoded information can be changed after creation. This dynamic QR code has a unique short redirection URL that points to the destination URL where the content is hosted.
- Dynamic QR codes have tracking capabilities that allow for tracking of scanning and usage.
- The scanning process for a QR code involves detecting the three position markers, mode indicator, character count indicator, encoded error correction data, and encoded information in order to retrieve the data and convert it to its original form.
- QR codes are useful for a variety of purposes, such as digital menus, business cards, authentication, payments, and more.
 "https://theconversation.com/how-qr-codes-work-and-what-makes-them-dangerous-a-computer-scientist-explains-177217"
"https://theconversation.com/how-qr-codes-work-and-what-makes-them-dangerous-a-computer-scientist-explains-177217"
- QR codes are similar to barcodes, but they can store much more data by encoding it in both vertical and horizontal axes.
- QR codes are designed to be scanned using a smartphone camera, and their data can trigger an action on your phone.
- QR codes have the potential to help avoid contact with objects and close interactions with other people.
- QR codes can take you to phishing websites that try to trick you into entering your username or password for another site.
- QR codes could take you to a legitimate website and trick that website into doing something harmful, such as giving an attacker access to your account.
- Some URLs stored in QR codes might ultimately take you to a malicious website that tricks another website you are logged into on the same device to take an unauthorized action.
- The app used to scan the QR code could contain a vulnerability that allows malicious QR codes to take over your device even if you don’t click the link stored in it.
- To avoid this threat, you should use trusted apps provided by the device manufacturer to scan QR codes and avoid downloading custom QR code apps.
- QR codes are composed of several parts: data, position markers, quiet zone and optional logos.
- The data in a QR code is a series of dots in a square grid, and each dot represents a one and each blank a zero in binary code.
- The patterns encoded in QR codes can represent numbers, letters, and URLs.
- With the smallest square grid being 21 rows by 21 columns, and the largest being 177 rows by 177 columns, QR codes can hold a lot of data.
- QR codes can use color or shape for the dots and background.
- Position markers are squares placed in a QR code’s top-left, top-right, and bottom-left corners, that help a smartphone camera or other device orient the QR code when scanning it.
- QR codes can include an optional logo in the middle, but it’s not actually part of the QR code and covers up some of its data.
- Due to the redundancy built into the QR code’s data, even if as much as 30% of the QR code is destroyed or difficult to read, the data can still be recovered.
- To avoid risks associated with visiting malicious URLs, you should ensure that the URL is safe and comes from a trusted source before opening the link stored in the QR code.
- Simply because the QR code has a logo you recognize, it doesn’t mean you should click on the URL it contains.
 "ELI5: When people create QR/Bar Codes, how do they avoid duplication?"
"ELI5: When people create QR/Bar Codes, how do they avoid duplication?"
- QR and bar codes are used to encode information
- When a QR code is scanned, the dots on the code represent the URL or contact information that is displayed
- Duplicate QR codes can be created for the same tag; encoding the same data can result in the same QR code, but otherwise they will be different
- Barcodes, in general, are a string of numbers in picture form
- Companies have a range of numbers assigned to them for the purpose of unique identification
- GS1 manages the common barcodes used in stores; the organization assigns a 3-digit prefix to member organizations in different countries to manage the assignment of a 9-digit range
- The first few digits in a barcode indicate the prefix allocated to member organizations in different countries
- The national organization then has the authority to give part of the range of different digits to companies
- The first product a company has may have the number 001, and the total barcode will store the number 3831234320018 (the last digit, 8, is the calculated check digit)
- Changing one letter in a QR code will produce a different code
- QR codes have 3.4*10^7111 possible combinations
- An observable universe has 1 × 10^(80) particles, so QR codes have significantly more possible combinations
- QR codes are generally used to store URLs to access different websites
- The target URL can be stored in the QR code without actually visiting the website
- The complexity of a QR code can handle images to add color, text or image and geo-location information, all with the possibility of making it possible for social media interaction
- The downside to a QR code is that it may be duplicated and others could replace the original URL
- The most common use cases for barcodes are inventory and POS systems
- POS systems use barcodes to scan for information on price and inventory
- Inventory management uses barcodes to track products
- A barcode is a low-tech version of a digital copy machine which reads the string of numbers when scanned
- The barcode contains a string of 12 random numbers (0-9) and the organization of the numbers tells the register what item is being scanned and its price
- The first six digits of barcodes are set aside for most companies
- Philips light bulbs use barcode number 046677 which helps in identifying the specific product
 "https://www.qrcode.com/en/about/standards.html"
"https://www.qrcode.com/en/about/standards.html"
- Denso Wave wishes for QR code to be used by as many people as possible; they published the specifications publicly.
- QR code is standardized based on respective national or international standards.
- QR code was approved as an international standard in June 2000, ensuring widespread acceptance not only in Japan, but also internationally.
- Denso Wave has waived the rights to a patent in its possession (Patent No. 2938338) for standardized QR Codes only.
- QR code size grows by four modules per side, from 21 x 21 modules to 177 x 177 modules.
- QR code can hold alphanumeric, numeric, 8-bit bytes, and Kanji characters.
-
QR code’s maximum capacity depends on the character type and error correction level. The capacities are:
- Numeric: max 7,089 characters
- Alphanumeric: max 4,296 characters
- 8-bit bytes (binary): max 2,953 characters
- Kanji: max 1,817 characters
- QR code’s error correction level is classified into four: Level L, M, Q, and H.
- Depending on the error correction level, approximately 7-30% of codewords can be restored.
- Structured appending is available in QR code, which allows printing up to 16 symbols even in a small area.
- The QR code specification can be purchased from ISO/IEC organization, which established QR code as an ISO standard.
💭 Looking into
Discuss the applications of QR codes
💭 Looking into
Explains what a QR code is and what it does