March 10, 2023
stages of medical care for complete rupture of the middle - diaphragmatic vein
Words
903
Time
2m 6s
Contributors
35
Words read
11.1k
Have an opinion? Send us proposed edits/additions and we may incorporate them into this article with credit.
Endoscopy
cauterization
liver transplant
transfusions
dialysis
All answers
Prevention
Treatment
Surgery
Hemodialysis
Endoscopic Exam
Jump to top
Research
 Source: "Blown Vein: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Pr..." (from web, www.healthline.com)
Source: "Blown Vein: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Pr..." (from web, www.healthline.com)
-
Prevention of complete rupture of the middle - diaphragmatic vein:
- Drink plenty of water before going for blood work or IV insertion, and inform your healthcare provider of any previous problems with your veins.
- Choose the best vein available and identify the correct size of needle for that vein.
- Avoid the area where veins divert. If it’s hard to find a vein, they should ask you to make a fist.
- Use a tourniquet or other device to make the vein more visible. For older adults, a blood pressure cuff may be preferable to the tourniquet. If a tourniquet is used, it shouldn’t be too tight.
- Insert the needle at a 30-degree angle or less.
- Stabilize the vein by applying a thumb below the puncture site.
- Take a slow, steady approach.
- Release the tourniquet before withdrawing the needle.
- Carefully withdraw the needle and apply gentle pressure to the site.
-
Treatment of complete rupture of the middle - diaphragmatic vein:
- Needle must be removed.
- Healthcare provider typically applies a little pressure to the injection site to minimize blood loss and swelling.
- After a few minutes, they clean the area to prevent infection.
- If there’s a lot of swelling, an ice pack can help ease symptoms.
- Vein should not be used again until it’s healed.
- Collapsed veins can heal, but some never bounce back. Depending on the location of the vein, this can lead to circulation problems. New blood vessels will develop to bypass the collapsed vein.
- In some cases, medication that was to be delivered intravenously can be potentially harmful when spilled into the skin. When that happens, further treatment may be required.
 Source: "Esophageal varices - Diagnosis and treatment - ..." (from web, www.mayoclinic.org)
Source: "Esophageal varices - Diagnosis and treatment - ..." (from web, www.mayoclinic.org)
-
Endoscopic exam
- A procedure called upper gastrointestinal endoscopy is the preferred method of screening for esophageal varices
- Doctor inserts a thin, flexible, lighted tube (endoscope) through the mouth and into the esophagus, stomach and the beginning of the small intestine (duodenum)
- Doctor will look for dilated veins, measure them, if found, and check for red streaks and red spots
- Treatment can be performed during the exam
-
Medications to reduce pressure in the portal vein
- Beta blockers such as propranolol (Inderal, Innopran XL) and nadolol (Corgard) can help reduce blood pressure in the portal vein, decreasing the likelihood of bleeding
-
Using elastic bands to tie off bleeding veins
- Endoscopic band ligation is an option for people with a high risk of bleeding, or who have had bleeding from varices before
- Using an endoscope, the doctor uses suction to pull the varices into a chamber at the end of the scope and wraps them with an elastic band, essentially “strangling” the veins so they can’t bleed
-
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS)
- Involves creating an opening between the portal vein and the hepatic vein, which carries blood from the liver to the heart
- Reduces pressure in the portal vein and often stops bleeding from esophageal varices
- Can cause serious complications, such as liver failure and mental confusion
-
Balloon tamponade
- Involves inflating a balloon to put pressure on the varices for up to 24 hours
- Carries a high risk of bleeding recurrence after the balloon is deflated
- Can also cause serious complications, such as a rupture in the esophagus
-
Transfusion
- To replace lost blood and a clotting factor to stop bleeding
-
Antibiotics
- To prevent infection
-
Liver transplant
- An option for people with severe liver disease or those who experience recurrent bleeding of esophageal varices
-
Beta blockers and endoscopic band ligation
- Recommended treatments to help prevent re-bleeding
-
Experimental emergency therapy
- Involves spraying an adhesive powder on the esophagus to stick to the varices and may
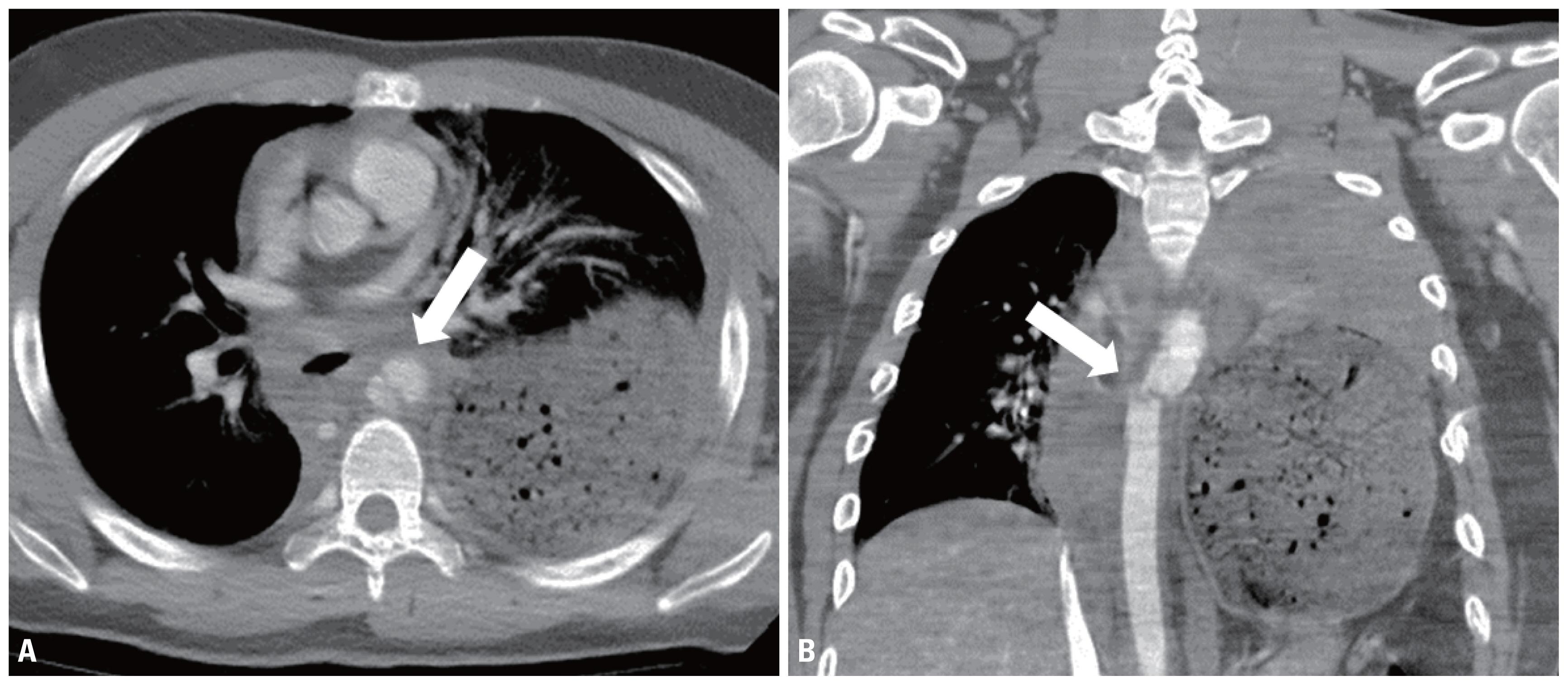
 Source: "Diaphragmatic rupture: a frequently missed inju..." (from web, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
Source: "Diaphragmatic rupture: a frequently missed inju..." (from web, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
-
Computed tomography:
- CT is the imaging modality of choice in the assessment of patients with clinical or radiographic findings suggestive of DR.
- CT of blunt diaphragmatic rupture.
- Imaging of diaphragmatic injuries.
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging:
- Can invasive diagnostic methods be reduced by magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of diaphragmatic injuries in left thoracoabdominal penetrating injuries?
-
FAST scan
- FAST scan in the diagnosis of acute diaphragmatic rupture.
 Source: "TIPS procedure - Cirrhosis" (from reddit, r/surgery)
Source: "TIPS procedure - Cirrhosis" (from reddit, r/surgery)
-
TIPS procedure
- Creates a shunt between the high pressure portal system and the rest of the body’s venous system which significantly drops the portal pressure and can improve ascites dramatically
- More effective than large volume paracentesis for controlling ascites
- Major benefit in ascites control and modest survival benefit
- Hepatic encephalopathy unfortunately increases slightly in risk after TIPS
- Complications rates are largely dependent on the operator & technique but overall are acceptably low
- Universal risks to any procedure - bleeding, infection, injury to nearby structures, failure of the procedure and need for further procedures
-
Large Volume Paracentesis
- 42% recurrence after TIPS vs 89% recurrence after LVP
-
Other
- Hepatic encephalopathy can often be adequately controlled with lactulose and rifaximin
- Heart function often stabilizes within a few months
- Greatly reduces the risk of hemorrhage from ruptured esophageal varices
 Source: "2 weeks post op, AV Fistula for dialysis. Got t..." (from reddit, r/medizzy)
Source: "2 weeks post op, AV Fistula for dialysis. Got t..." (from reddit, r/medizzy)
-
Surgery
- Underwent surgery, stayed the night and did dialysis the next morning
- Had to raise the vein to the surface
- Complication of internal bleeding
-
Hemodialysis
- Tough
-
Complication beyond internal bleeding
- Fistula formation scars were small and not the entire length of the forearm
-
Use of Activase
- Not supposed to be used after surgery
- Clotted central line in chest
-
PICC or Central Line option
- Not suitable due to vessel placement
- Not gold standard as there are many complications and risks
-
Use of TPA
- Hella big no-no after surgery
- Platelet levels return to normal after about 30 minutes when Activase is bolused by mistake
💭 Looking into
What are the best practices for treating complete rupture of the middle - diaphragmatic vein?
💭 Looking into
What are the long-term effects of complete rupture of the middle - diaphragmatic vein?
💭 Looking into
What are the possible side effects of transfusions, dialysis, and medications for treating complete rupture of the middle - diaphragmatic vein?
💭 Looking into
What is the success rate of liver transplants for treating complete rupture of the middle - diaphragmatic vein?
💭 Looking into
What are the risks associated with endoscopy and cauterization of the veins?
 Source: "Diaphragmatic rupture | definition of ... - Med..." (from web, medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com)
Source: "Diaphragmatic rupture | definition of ... - Med..." (from web, medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com)
-
Stabilization without delay
- Nasogastric decompression
- Intubation
- Assisted ventilation with supplemental oxygen
-
Surgical repair of the hernia
- Invasion of the abdominal and thoracic cavities
-
Medical treatment
- Small meals of bland, easily digested food
- Moderate exercise
- Sleeping with the upper part of the body in a raised position
 Source: "Spontaneous diaphragmatic rupture: case report ..." (from web, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
Source: "Spontaneous diaphragmatic rupture: case report ..." (from web, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
None
 Source: "Liver cirrhosis; rupture of esophageal vein" (from reddit, r/AskDocs)
Source: "Liver cirrhosis; rupture of esophageal vein" (from reddit, r/AskDocs)
-
Treatment for complete rupture of the middle - diaphragmatic vein
- Initial treatment for a ruptured esophageal vein would involve an endoscopy and cauterization of the veins.
- In some cases, a liver transplant may be necessary if the rupture is severe enough.
- Additional treatment may include transfusions, dialysis, and medications to manage any symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy.
💭 Looking into
What is the best medical care for a complete rupture of the middle diaphragmatic vein?